Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis to enhance the growth of maize under saline conditions
Keywords:
Auxin production, Bacillus subtilis, Indole-3-acetic acid, Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, Salt stressAbstract
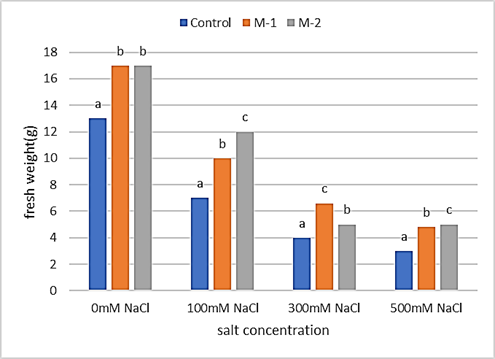
This study investigates the role of auxin-producing Bacillus subtilis in promoting the growth of Zea mays (L.) under saline conditions. Plant growth under bacterial inoculations was assessed through rooting assays and pot experiments. The results showed that the bacterial strains produced a significant amount of auxin at different concentrations of L-tryptophan. At 0 µg/mL, strain M-1 produces auxin at approximately 128 µg/mL, and at 500 µg/mL, strain M-2 produces 74 µg/mL of auxin. In pot trials, shoot length increased by 69% with the M-1 strain at 0 mM NaCl compared to the respective control. When salt treatment was given, the shoot length of M-2 was recorded at 26% at 100 mM NaCl, 26.3% at 300 mM NaCl, and 10% at 500 mM NaCl. At 0 mM NaCl, the M-1 and M-2 strains produced a fresh weight of 30.7%. At 100 mM and 500 mM NaCl, the fresh weight of M-2 was recorded as 71.4% and 66.6%, respectively. At 300 mM NaCl, M-1 showed an improved wet weight of 65%. Similarly, at 0 mM NaCl, the M-1 and M-2 strains recorded an approximately 1-fold increase in dry weight compared to the control. However, at a higher salinity level (500 mM NaCl), the dry weight increased by around 16% compared to the respective control. The results of this study showed that the strains of B. subtilis have the potential to mitigate the salinity of maize plants under saline conditions.
Downloads
References
Azeem, M., Haider, M.Z., Javed, S., Saleem, M.H., & Alatawi, A. (2022). Drought stress amelioration in maize (Zea mays L.) by inoculation of Bacillus spp. strains under sterile soil conditions. Agriculture, 12:50, 1–21.
Badu-Apraku, B., & Fakorede, M.A.B. (2017). Morphology and physiology of maize. In: Advances in Genetic Enhancement of Early and Extra-Early Maize for Sub-Saharan Africa, 33–53.
Bolivar-Anillo, H.J., González-Rodríguez, V.E., Cantoral, J.M., García-Sánchez, D., Collado, I.G., & Garrido, C. (2021). Endophytic bacteria Bacillus subtilis, isolated from Zea mays, as potential biocontrol agent against Botrytis cinerea. Biology, 10:492, 1–26.
Dashti, N., Al-Sarraf, N.Y.A., Cherian, V.M., & Montasser, M.S. (2021). Isolation and characterization of novel plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) isolates from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) rhizospherical soil: A novel IAA-producing bacteria. Kuwait Journal of Science, 48(2):1–18.
Javoreková, S., Cinkocki, R., Maková, J., & Hricáková, N. (2020). Isolation and identification of rhizobacteria from maize (Zea mays L.) in Luvisols and documentation of their plant growth-promoting traits. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences, 10(3): 505-510.
Katsenios, N., Andreou, V., Sparangis, P., Djordjevic, N., Giannoglou, M., Chanioti, S., Kasimatis, C.-N., Kakabouki, I., Leonidakis, D., Danalatos, N., Katsaros, G., & Efthimiadou, A. (2022). Assessment of plant growth-promoting bacteria strains on growth, yield, and quality of sweet corn. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 11598.
Navid, S., Tanveer, S. & Ali, B. (2023). Auxin production by Bacillus simplex enhanced the growth of Zea mays (L.) under in-vitro and in-vivo conditions. LGU Journal of Life Sciences, 7(4): 457-471.
Shah, D., Khan, M.S., Aziz, S., Ali, H., & Pecoraro, L. (2022). Molecular and biochemical characterization, antimicrobial activity, stress tolerance, and plant growth-promoting effect of endophytic bacteria isolated from wheat varieties. Microorganisms, 10:21, 1–17.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Masooma Saleh, Basharat Ali (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




